Difference between revisions of "Example Calibrate Planar Mono"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| (4 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
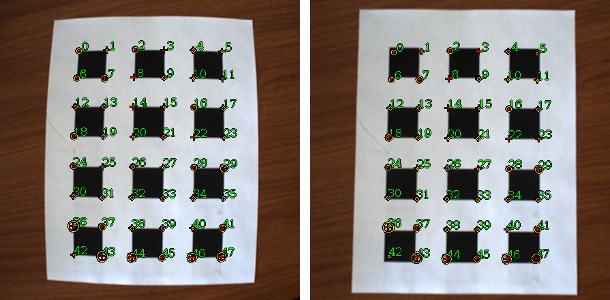
This example demonstrates how to use a high level calibration class that automatically detects calibration targets as viewed from a single (monocular) camera in a set of images. After processing the images the intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are saved to an XML file. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below. | This example demonstrates how to use a high level calibration class that automatically detects calibration targets as viewed from a single (monocular) camera in a set of images. After processing the images the intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are saved to an XML file. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below. | ||
Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/ | Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v1.1.0/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/calibration/ExampleCalibrateMonocular.java ExampleCalibrateMonocular.java] | ||
Calibration Tutorial: [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration|Wikipage]] | Calibration Tutorial: [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration|Wikipage]] | ||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
* should be covered. | * should be covered. | ||
* | * | ||
* After processing both intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are estimated. | * After processing both intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are estimated. Square grid and chessboard | ||
* targets are demonstrated by this example. See calibration tutorial for a discussion of different target types | * targets are demonstrated by this example. See calibration tutorial for a discussion of different target types | ||
* and how to collect good calibration images. | * and how to collect good calibration images. | ||
* | * | ||
* All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateMonoPlanar}. | * All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateMonoPlanar}. The code below | ||
* loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. | * loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. See in code comments for tuning | ||
* and implementation issues. | * and implementation issues. | ||
* | * | ||
* @author Peter Abeles | |||
* @see CalibrateMonoPlanar | * @see CalibrateMonoPlanar | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public class ExampleCalibrateMonocular { | public class ExampleCalibrateMonocular { | ||
public static void main( String[] args ) { | public static void main( String[] args ) { | ||
DetectSingleFiducialCalibration detector; | |||
List<String> images; | List<String> images; | ||
// Regular Circle Example | // Regular Circle Example | ||
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleRegularGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(8, 10, 1.5, 2.5)); | // detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleRegularGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 8, /*numCols*/ 10, 1.5, 2.5)); | ||
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleRegular"),"image", null); | // images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleRegular"),"image", null); | ||
// Hexagonal Circle Example | // Hexagonal Circle Example | ||
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleHexagonalGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(24, 28, 1, 1.2)); | // detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleHexagonalGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 24, /*numCols*/ 28, 1, 1.2)); | ||
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleHexagonal"),"image", null); | // images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleHexagonal"),"image", null); | ||
// Square Grid example | // Square Grid example | ||
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(4, 3, 30, 30)); | // detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 4, /*numCols*/ 3, 30, 30)); | ||
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square"),"left", null); | // images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square"),"left", null); | ||
// ECoCheck Example | |||
// detector = new MultiToSingleFiducialCalibration(FactoryFiducialCalibration. | |||
// ecocheck(null, ConfigECoCheckMarkers. | |||
// singleShape(/*numRows*/ 9, /*numCols*/ 7, /*num markers*/ 1, /* square size */ 30))); | |||
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Zed_ecocheck"), "left", null); | |||
// Chessboard Example | // Chessboard Example | ||
detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null,new ConfigGridDimen(7, 5, 30)); | detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null, | ||
images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"),"left", null); | new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 7,/*numCols*/ 5,/*shapeSize*/ 30)); | ||
images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"), "left", null); | |||
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm | // Declare and setup the calibration algorithm | ||
var calibrator = new CalibrateMonoPlanar(); | |||
// tell it type type of target and which intrinsic parameters to estimate | |||
calibrator.configurePinhole( | |||
/*assumeZeroSkew*/ true, | |||
/*numRadialParam*/ 2, | |||
/*includeTangential*/ false); | |||
// tell it | var usedImages = new ArrayList<String>(); | ||
for (String n : images) { | |||
BufferedImage input = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(n); | |||
GrayF32 image = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(input, (GrayF32)null); | |||
if (detector.process(image)) { | |||
// Need to tell it the image shape and the layout once | |||
if (usedImages.isEmpty()) | |||
calibrator.initialize(image.getWidth(), image.getHeight(), List.of(detector.getLayout())); | |||
calibrator.addImage(detector.getDetectedPoints().copy()); | |||
usedImages.add(n); | |||
} else { | |||
System.err.println("Failed to detect target in " + n); | |||
} else { | |||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
// process and compute intrinsic parameters | // process and compute intrinsic parameters | ||
CameraPinholeBrown intrinsic = | CameraPinholeBrown intrinsic = calibrator.process(); | ||
// save results to a file and print out | // save results to a file and print out | ||
CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "intrinsic.yaml"); | CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "intrinsic.yaml"); | ||
System.out.println(calibrator.computeQualityText(usedImages)); | |||
System.out.println(); | System.out.println(); | ||
System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---"); | System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---"); | ||
Latest revision as of 18:05, 9 September 2023
This example demonstrates how to use a high level calibration class that automatically detects calibration targets as viewed from a single (monocular) camera in a set of images. After processing the images the intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are saved to an XML file. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below.
Example File: ExampleCalibrateMonocular.java
Calibration Tutorial: Wikipage
Concepts:
- Camera calibration
- Lens distortion
- Intrinsic parameters
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Example of how to calibrate a single (monocular) camera using a high level interface. Depending on the calibration
* target detector and target type, the entire target might need to be visible in the image. All camera images
* should be in focus and that target evenly spread through out the images. In particular the edges of the image
* should be covered.
*
* After processing both intrinsic camera parameters and lens distortion are estimated. Square grid and chessboard
* targets are demonstrated by this example. See calibration tutorial for a discussion of different target types
* and how to collect good calibration images.
*
* All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateMonoPlanar}. The code below
* loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. See in code comments for tuning
* and implementation issues.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
* @see CalibrateMonoPlanar
*/
public class ExampleCalibrateMonocular {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
DetectSingleFiducialCalibration detector;
List<String> images;
// Regular Circle Example
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleRegularGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 8, /*numCols*/ 10, 1.5, 2.5));
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleRegular"),"image", null);
// Hexagonal Circle Example
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.circleHexagonalGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 24, /*numCols*/ 28, 1, 1.2));
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/mono/Sony_DSC-HX5V_CircleHexagonal"),"image", null);
// Square Grid example
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 4, /*numCols*/ 3, 30, 30));
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square"),"left", null);
// ECoCheck Example
// detector = new MultiToSingleFiducialCalibration(FactoryFiducialCalibration.
// ecocheck(null, ConfigECoCheckMarkers.
// singleShape(/*numRows*/ 9, /*numCols*/ 7, /*num markers*/ 1, /* square size */ 30)));
// images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Zed_ecocheck"), "left", null);
// Chessboard Example
detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null,
new ConfigGridDimen(/*numRows*/ 7,/*numCols*/ 5,/*shapeSize*/ 30));
images = UtilIO.listByPrefix(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"), "left", null);
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm
var calibrator = new CalibrateMonoPlanar();
// tell it type type of target and which intrinsic parameters to estimate
calibrator.configurePinhole(
/*assumeZeroSkew*/ true,
/*numRadialParam*/ 2,
/*includeTangential*/ false);
var usedImages = new ArrayList<String>();
for (String n : images) {
BufferedImage input = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(n);
GrayF32 image = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(input, (GrayF32)null);
if (detector.process(image)) {
// Need to tell it the image shape and the layout once
if (usedImages.isEmpty())
calibrator.initialize(image.getWidth(), image.getHeight(), List.of(detector.getLayout()));
calibrator.addImage(detector.getDetectedPoints().copy());
usedImages.add(n);
} else {
System.err.println("Failed to detect target in " + n);
}
}
// process and compute intrinsic parameters
CameraPinholeBrown intrinsic = calibrator.process();
// save results to a file and print out
CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "intrinsic.yaml");
System.out.println(calibrator.computeQualityText(usedImages));
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---");
System.out.println();
intrinsic.print();
}
}