Difference between revisions of "Example Rectification Calibrated"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to search (Created page with "= Rectification of Calibrated Stereo = <center> <gallery heights=190 widths=550 > Image:Example_unrectified.jpg|Before rectification features are not aligned along the y-axis...") |
m |
||
| (23 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<gallery heights=190 widths=550 > | <gallery heights=190 widths=550 > | ||
| Line 8: | Line 6: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
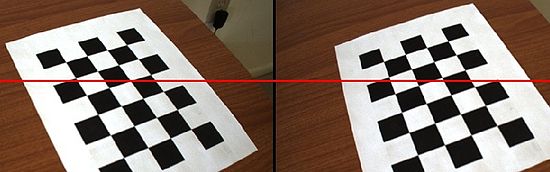
Stereo rectification is the process of distorting an image such that the epipoles of both images are at infinity. | Stereo rectification is the process of distorting an image such that the epipoles of both images are at infinity. If the epipoles are at infinity along the x-axis, then corresponding features must lie along the same y-coordinates. Using knowledge that correspondence feature's have the same y-coordinate allows for quick searches. Many stereo vision algorithm rely on rectification. The example below demonstrates rectification for a calibrated stereo pair. Note that after calibration the new camera view has a different set of intrinsic parameters. | ||
Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/ | Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.39/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/stereo/ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo.java ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo.java] | ||
Concepts: | Concepts: | ||
* Stereo Rectification | * Stereo Rectification | ||
* Stereo Vision | * Stereo Vision | ||
Related Examples: | Related Examples: | ||
* [[Example_Calibrate_Planar_Stereo| Stereo Camera Calibration]] | * [[Example_Calibrate_Planar_Stereo| Stereo Camera Calibration]] | ||
* [[Example_Remove_Lens_Distortion| Removing Lens Distortion]] | * [[Example_Remove_Lens_Distortion| Removing Lens Distortion]] | ||
| Line 27: | Line 21: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* | * Shows how to rectify a pair of stereo images with known intrinsic parameters and stereo baseline. When you | ||
* rectify a stereo pair you are applying a transform that removes lens distortion and "rotates" the views | |||
* The example code does the following:< | * such that they are parallel to each other, facilitating stereo processing. | ||
* | * | ||
* | * The example code does the following: | ||
* <ol> | |||
* | * <li>Load stereo extrinsic and intrinsic parameters from a file along with a pair of images.</li> | ||
* | * <li>Undistort and rectify images. This provides one rectification matrix for each image along with a new | ||
* </ | * camera calibration matrix.</li> | ||
* <li>The original rectification does not try to maximize view area, however it can be adjusted.</li> | |||
* <li>After rectification is finished the results are displayed.</li> | |||
* </ol> | |||
* | * | ||
* Note that the y-axis in left and right images align after rectification. You can click in the images to draw a line | |||
* Note that the y-axis in left and right images align after rectification. The curved image | * that makes this easy to see. The curved image birder is an artifact of lens distortion being removed. | ||
* | * | ||
* @author Peter Abeles | * @author Peter Abeles | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public class ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo { | public class ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo { | ||
public static void main( String[] args ) { | |||
String dir = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess/"); | |||
StereoParameters param = CalibrationIO.load(new File(dir, "stereo.yaml")); | |||
StereoParameters param = | |||
// load images | // load images | ||
BufferedImage origLeft = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir | BufferedImage origLeft = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "left05.jpg"); | ||
BufferedImage origRight = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir | BufferedImage origRight = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "right05.jpg"); | ||
// distorted images | // distorted images | ||
Planar<GrayF32> distLeft = | |||
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origLeft, null, true, GrayF32.class); | |||
Planar<GrayF32> distRight = | |||
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origRight, null, true, GrayF32.class); | |||
// storage for undistorted + rectified images | // storage for undistorted + rectified images | ||
Planar<GrayF32> rectLeft = distLeft.createSameShape(); | |||
Planar<GrayF32> rectRight = distRight.createSameShape(); | |||
// Compute rectification | // Compute rectification | ||
| Line 74: | Line 64: | ||
// original camera calibration matrices | // original camera calibration matrices | ||
DMatrixRMaj K1 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getLeft(), (DMatrixRMaj)null); | |||
DMatrixRMaj K2 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getRight(), (DMatrixRMaj)null); | |||
rectifyAlg.process(K1,new Se3_F64(),K2,leftToRight); | rectifyAlg.process(K1, new Se3_F64(), K2, leftToRight); | ||
// rectification matrix for each image | // rectification matrix for each image | ||
DMatrixRMaj rect1 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels1(); | |||
DMatrixRMaj rect2 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels2(); | |||
// New calibration matrix, | // New calibration matrix, | ||
// Both cameras have the same one after rectification. | // Both cameras have the same one after rectification. | ||
DMatrixRMaj rectK = rectifyAlg.getCalibrationMatrix(); | |||
// Adjust the rectification to make the view area more useful | // Adjust the rectification to make the view area more useful | ||
RectifyImageOps.fullViewLeft(param.left | RectifyImageOps.fullViewLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null); | ||
// RectifyImageOps.allInsideLeft(param.left | // RectifyImageOps.allInsideLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null); | ||
// undistorted and rectify images | // undistorted and rectify images | ||
ImageDistort< | var rect1_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3); // TODO simplify code some how | ||
var rect2_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3); | |||
ImageDistort< | ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect1, rect1_F32); | ||
ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect2, rect2_F32); | |||
ImageDistort<Planar<GrayF32>, Planar<GrayF32>> rectifyImageLeft = | |||
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getLeft(), rect1_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distLeft.getImageType()); | |||
ImageDistort<Planar<GrayF32>, Planar<GrayF32>> rectifyImageRight = | |||
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getRight(), rect2_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distRight.getImageType()); | |||
rectifyImageLeft.apply(distLeft, rectLeft); | |||
rectifyImageRight.apply(distRight, rectRight); | |||
// convert for output | // convert for output | ||
BufferedImage outLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectLeft,null); | BufferedImage outLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectLeft, null, true); | ||
BufferedImage outRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectRight, null); | BufferedImage outRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectRight, null, true); | ||
// show results and draw a horizontal line where the user clicks to see rectification easier | // show results and draw a horizontal line where the user clicks to see rectification easier | ||
var panel = new ListDisplayPanel(); | |||
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, origLeft, origRight), "Original"); | panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, origLeft, origRight), "Original"); | ||
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, outLeft, outRight), "Rectified"); | panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, outLeft, outRight), "Rectified"); | ||
ShowImages.showWindow(panel,"Stereo Rectification Calibrated"); | ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Stereo Rectification Calibrated", true); | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 19:31, 8 October 2021
Stereo rectification is the process of distorting an image such that the epipoles of both images are at infinity. If the epipoles are at infinity along the x-axis, then corresponding features must lie along the same y-coordinates. Using knowledge that correspondence feature's have the same y-coordinate allows for quick searches. Many stereo vision algorithm rely on rectification. The example below demonstrates rectification for a calibrated stereo pair. Note that after calibration the new camera view has a different set of intrinsic parameters.
Example File: ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo.java
Concepts:
- Stereo Rectification
- Stereo Vision
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Shows how to rectify a pair of stereo images with known intrinsic parameters and stereo baseline. When you
* rectify a stereo pair you are applying a transform that removes lens distortion and "rotates" the views
* such that they are parallel to each other, facilitating stereo processing.
*
* The example code does the following:
* <ol>
* <li>Load stereo extrinsic and intrinsic parameters from a file along with a pair of images.</li>
* <li>Undistort and rectify images. This provides one rectification matrix for each image along with a new
* camera calibration matrix.</li>
* <li>The original rectification does not try to maximize view area, however it can be adjusted.</li>
* <li>After rectification is finished the results are displayed.</li>
* </ol>
*
* Note that the y-axis in left and right images align after rectification. You can click in the images to draw a line
* that makes this easy to see. The curved image birder is an artifact of lens distortion being removed.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
String dir = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess/");
StereoParameters param = CalibrationIO.load(new File(dir, "stereo.yaml"));
// load images
BufferedImage origLeft = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "left05.jpg");
BufferedImage origRight = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "right05.jpg");
// distorted images
Planar<GrayF32> distLeft =
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origLeft, null, true, GrayF32.class);
Planar<GrayF32> distRight =
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origRight, null, true, GrayF32.class);
// storage for undistorted + rectified images
Planar<GrayF32> rectLeft = distLeft.createSameShape();
Planar<GrayF32> rectRight = distRight.createSameShape();
// Compute rectification
RectifyCalibrated rectifyAlg = RectifyImageOps.createCalibrated();
Se3_F64 leftToRight = param.getRightToLeft().invert(null);
// original camera calibration matrices
DMatrixRMaj K1 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getLeft(), (DMatrixRMaj)null);
DMatrixRMaj K2 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getRight(), (DMatrixRMaj)null);
rectifyAlg.process(K1, new Se3_F64(), K2, leftToRight);
// rectification matrix for each image
DMatrixRMaj rect1 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels1();
DMatrixRMaj rect2 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels2();
// New calibration matrix,
// Both cameras have the same one after rectification.
DMatrixRMaj rectK = rectifyAlg.getCalibrationMatrix();
// Adjust the rectification to make the view area more useful
RectifyImageOps.fullViewLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null);
// RectifyImageOps.allInsideLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null);
// undistorted and rectify images
var rect1_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3); // TODO simplify code some how
var rect2_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3);
ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect1, rect1_F32);
ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect2, rect2_F32);
ImageDistort<Planar<GrayF32>, Planar<GrayF32>> rectifyImageLeft =
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getLeft(), rect1_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distLeft.getImageType());
ImageDistort<Planar<GrayF32>, Planar<GrayF32>> rectifyImageRight =
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getRight(), rect2_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distRight.getImageType());
rectifyImageLeft.apply(distLeft, rectLeft);
rectifyImageRight.apply(distRight, rectRight);
// convert for output
BufferedImage outLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectLeft, null, true);
BufferedImage outRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectRight, null, true);
// show results and draw a horizontal line where the user clicks to see rectification easier
var panel = new ListDisplayPanel();
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, origLeft, origRight), "Original");
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, outLeft, outRight), "Rectified");
ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Stereo Rectification Calibrated", true);
}
}