Difference between revisions of "Example Detect Calibration Target"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to search (Added image) |
m |
||
| (24 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<gallery heights=300 widths=610 > | <gallery heights=300 widths=610 > | ||
| Line 9: | Line 7: | ||
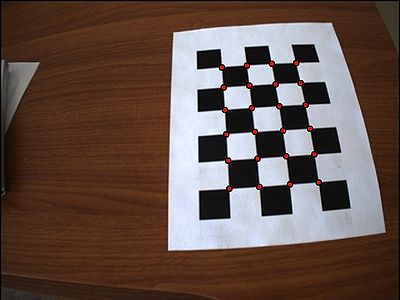
BoofCV provides fully automated calibration target detection. Once detected calibration point locations are returned with a high level of precision. While intended for camera calibration, they can also be used for other applications, such as augmented reality. In this example it is demonstrated how to detect different types of grid based targets. | BoofCV provides fully automated calibration target detection. Once detected calibration point locations are returned with a high level of precision. While intended for camera calibration, they can also be used for other applications, such as augmented reality. In this example it is demonstrated how to detect different types of grid based targets. | ||
Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/ | Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.40/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/calibration/ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints.java ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints.java] | ||
Concepts: | Concepts: | ||
* | * Fiducials / Markers | ||
* Calibration | |||
* | |||
Related Examples/Tutorials: | Related Examples/Tutorials: | ||
* [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration| Tutorial Camera Calibration]] | * [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration| Tutorial Camera Calibration]] | ||
* [[Papers_and_Reports | Chessboard Detector Paper]] | |||
Videos: | |||
* [https://youtu.be/qMTtdiujAtQ?t=236 Circle Asymmetric Grid] | |||
* [https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8pn9Ebw90uk&t=740s X-Corner Chessboard Detector] | |||
= Example Code = | = Example Code = | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* Example that demonstrates how to detect targets | * Example that demonstrates how to detect calibration targets. Calibration points are found on the | ||
* | * targets to a high level of precision. It is assumed that a single image only shows a single target | ||
* and that the entire target is visible. If these conditions are not meet then the target is likely | |||
* to not be detected. | |||
* | * | ||
* @author Peter Abeles | * @author Peter Abeles | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public class ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints { | public class ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints { | ||
public static void main( String[] args ) { | |||
public static void main( String | |||
// load the test image | // load the test image | ||
// String directory = " | // String directory = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square"); | ||
String directory = " | String directory = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"); | ||
BufferedImage orig = UtilImageIO. | BufferedImage orig = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(directory + "/left01.jpg"); | ||
GrayF32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(orig, (GrayF32)null); | |||
// To select different types of detectors add or remove comments below | // To select different types of detectors add or remove comments below | ||
DetectSingleFiducialCalibration detector; | |||
// For chessboard targets, tune RADIUS parameter for your images | // For chessboard targets, tune RADIUS parameter for your images | ||
// detector = | // detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(4, 3, 30, 30)); | ||
detector = | detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*rows*/ 7, /*cols*/ 5, /*shape size*/ 30)); | ||
// process the image and check for failure condition | // process the image and check for failure condition | ||
if( !detector.process(input) ) | if (!detector.process(input)) | ||
throw new RuntimeException("Target detection failed!"); | throw new RuntimeException("Target detection failed!"); | ||
// Ordered observations of calibration points on the target | // Ordered observations of calibration points on the target | ||
CalibrationObservation set = detector.getDetectedPoints(); | |||
// render and display the results | // render and display the results | ||
Graphics2D g2 = orig.createGraphics(); | Graphics2D g2 = orig.createGraphics(); | ||
for( | for (PointIndex2D_F64 p : set.points) | ||
VisualizeFeatures.drawPoint(g2, | VisualizeFeatures.drawPoint(g2, p.p.x, p.p.y, 3, Color.RED, true); | ||
ShowImages.showWindow(orig,"Calibration Points"); | ShowImages.showWindow(orig, "Calibration Points", true); | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:24, 17 January 2022
BoofCV provides fully automated calibration target detection. Once detected calibration point locations are returned with a high level of precision. While intended for camera calibration, they can also be used for other applications, such as augmented reality. In this example it is demonstrated how to detect different types of grid based targets.
Example File: ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints.java
Concepts:
- Fiducials / Markers
- Calibration
Related Examples/Tutorials:
Videos:
Example Code
/**
* Example that demonstrates how to detect calibration targets. Calibration points are found on the
* targets to a high level of precision. It is assumed that a single image only shows a single target
* and that the entire target is visible. If these conditions are not meet then the target is likely
* to not be detected.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleDetectCalibrationPoints {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
// load the test image
// String directory = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square");
String directory = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess");
BufferedImage orig = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(directory + "/left01.jpg");
GrayF32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(orig, (GrayF32)null);
// To select different types of detectors add or remove comments below
DetectSingleFiducialCalibration detector;
// For chessboard targets, tune RADIUS parameter for your images
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(4, 3, 30, 30));
detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null, new ConfigGridDimen(/*rows*/ 7, /*cols*/ 5, /*shape size*/ 30));
// process the image and check for failure condition
if (!detector.process(input))
throw new RuntimeException("Target detection failed!");
// Ordered observations of calibration points on the target
CalibrationObservation set = detector.getDetectedPoints();
// render and display the results
Graphics2D g2 = orig.createGraphics();
for (PointIndex2D_F64 p : set.points)
VisualizeFeatures.drawPoint(g2, p.p.x, p.p.y, 3, Color.RED, true);
ShowImages.showWindow(orig, "Calibration Points", true);
}
}