Difference between revisions of "Example Fit Polygon"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
Example Code: | Example Code: | ||
* [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0. | * [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.23/examples/src/boofcv/examples/features/ExampleFitPolygon.java ExampleFitPolygon.java] | ||
Concepts: | Concepts: | ||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
* Fits polygons to found contours around binary blobs. | * Fits polygons to found contours around binary blobs. | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public static void fitBinaryImage( | public static void fitBinaryImage(GrayF32 input) { | ||
GrayU8 binary = new GrayU8(input.width,input.height); | |||
BufferedImage polygon = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | BufferedImage polygon = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | ||
| Line 52: | Line 52: | ||
// reduce noise with some filtering | // reduce noise with some filtering | ||
GrayU8 filtered = BinaryImageOps.erode8(binary, 1, null); | |||
filtered = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(filtered, 1, null); | filtered = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(filtered, 1, null); | ||
| Line 86: | Line 86: | ||
* points can be a bit noisy compared to the others. | * points can be a bit noisy compared to the others. | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public static void fitCannyEdges( | public static void fitCannyEdges( GrayF32 input ) { | ||
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | ||
// Finds edges inside the image | // Finds edges inside the image | ||
CannyEdge< | CannyEdge<GrayF32,GrayF32> canny = | ||
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, | FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, GrayF32.class, GrayF32.class); | ||
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,null); | canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,null); | ||
| Line 122: | Line 122: | ||
* easier to deal with than working with Canny edges directly. | * easier to deal with than working with Canny edges directly. | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public static void fitCannyBinary( | public static void fitCannyBinary( GrayF32 input ) { | ||
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | ||
GrayU8 binary = new GrayU8(input.width,input.height); | |||
// Finds edges inside the image | // Finds edges inside the image | ||
CannyEdge< | CannyEdge<GrayF32,GrayF32> canny = | ||
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, false, true, | FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, false, true, GrayF32.class, GrayF32.class); | ||
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,binary); | canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,binary); | ||
| Line 156: | Line 156: | ||
// load and convert the image into a usable format | // load and convert the image into a usable format | ||
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("shapes/shapes02.png")); | BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("shapes/shapes02.png")); | ||
GrayF32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromSingle(image, null, GrayF32.class); | |||
gui.addImage(image,"Original"); | gui.addImage(image,"Original"); | ||
Revision as of 21:22, 27 March 2016
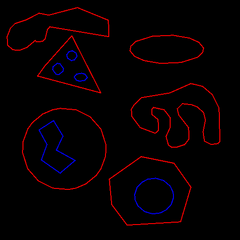
Demonstration for how to fit a polygon to object contours and edges. The input contours can be found from binary blobs and the edge sequence from Canny edge detector. This is often a useful preprocessing step before applying a higher level image processing algorithm.
Example Code:
Concepts:
- Object contours/edges
- Shape fitting
Relevant Applets:
Example Code
/**
* Demonstration of how to convert a point sequence describing an objects outline/contour into a sequence of line
* segments. Useful when analysing shapes such as squares and triangles or when trying to simply the low level
* pixel output.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleFitPolygon {
// Polynomial fitting tolerances
static double splitFraction = 0.05;
static double minimumSideFraction = 0.1;
static ListDisplayPanel gui = new ListDisplayPanel();
/**
* Fits polygons to found contours around binary blobs.
*/
public static void fitBinaryImage(GrayF32 input) {
GrayU8 binary = new GrayU8(input.width,input.height);
BufferedImage polygon = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// the mean pixel value is often a reasonable threshold when creating a binary image
double mean = ImageStatistics.mean(input);
// create a binary image by thresholding
ThresholdImageOps.threshold(input, binary, (float) mean, true);
// reduce noise with some filtering
GrayU8 filtered = BinaryImageOps.erode8(binary, 1, null);
filtered = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(filtered, 1, null);
// Find the contour around the shapes
List<Contour> contours = BinaryImageOps.contour(filtered, ConnectRule.EIGHT,null);
// Fit a polygon to each shape and draw the results
Graphics2D g2 = polygon.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
for( Contour c : contours ) {
// Fit the polygon to the found external contour. Note loop = true
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(c.external,true,
splitFraction, minimumSideFraction,100);
g2.setColor(Color.RED);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
// handle internal contours now
g2.setColor(Color.BLUE);
for( List<Point2D_I32> internal : c.internal ) {
vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(internal,true, splitFraction, minimumSideFraction,100);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
}
}
gui.addImage(polygon, "Binary Blob Contours");
}
/**
* Fits a sequence of line-segments into a sequence of points found using the Canny edge detector. In this case
* the points are not connected in a loop. The canny detector produces a more complex tree and the fitted
* points can be a bit noisy compared to the others.
*/
public static void fitCannyEdges( GrayF32 input ) {
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// Finds edges inside the image
CannyEdge<GrayF32,GrayF32> canny =
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, GrayF32.class, GrayF32.class);
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,null);
List<EdgeContour> contours = canny.getContours();
Graphics2D g2 = displayImage.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
// used to select colors for each line
Random rand = new Random(234);
for( EdgeContour e : contours ) {
g2.setColor(new Color(rand.nextInt()));
for(EdgeSegment s : e.segments ) {
// fit line segments to the point sequence. Note that loop is false
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(s.points,false,
splitFraction, minimumSideFraction,100);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes, false, g2);
}
}
gui.addImage(displayImage, "Canny Trace");
}
/**
* Detects contours inside the binary image generated by canny. Only the external contour is relevant. Often
* easier to deal with than working with Canny edges directly.
*/
public static void fitCannyBinary( GrayF32 input ) {
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
GrayU8 binary = new GrayU8(input.width,input.height);
// Finds edges inside the image
CannyEdge<GrayF32,GrayF32> canny =
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, false, true, GrayF32.class, GrayF32.class);
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,binary);
List<Contour> contours = BinaryImageOps.contour(binary, ConnectRule.EIGHT, null);
Graphics2D g2 = displayImage.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
// used to select colors for each line
Random rand = new Random(234);
for( Contour c : contours ) {
// Only the external contours are relevant.
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(c.external,true,
splitFraction, minimumSideFraction,100);
g2.setColor(new Color(rand.nextInt()));
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
}
gui.addImage(displayImage, "Canny Contour");
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// load and convert the image into a usable format
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("shapes/shapes02.png"));
GrayF32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromSingle(image, null, GrayF32.class);
gui.addImage(image,"Original");
fitCannyEdges(input);
fitCannyBinary(input);
fitBinaryImage(input);
ShowImages.showWindow(gui, "Polygon from Contour", true);
}
}