Difference between revisions of "Example Calibrate Planar Mono"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to search (Created page) |
m |
||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<center> | <center> | ||
<gallery | <gallery heights=300 widths=610 > | ||
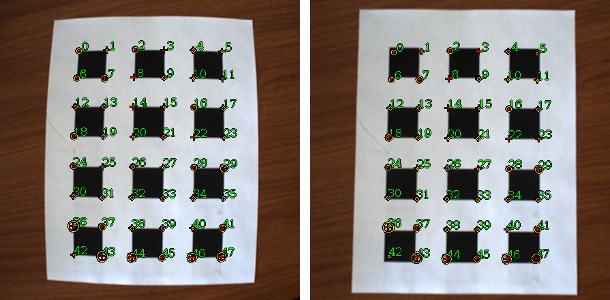
Image:Calib_mono.jpg| | Image:Calib_mono.jpg|Left uncalibrated. Right calibrated with lens distortion removed. Numbers are super imposed on the image to show calibration points. | ||
</gallery> | </gallery> | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
Revision as of 05:55, 18 April 2012
Monocular Camera Calibration with Planar Targets
Calibrating a monocular (single) camera is the process of learning its intrinsic camera parameters and removing lens distortion. This example demonstrates how to use multiple pictures of a planar calibration target. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below.
Example File: ExampleBinaryImage.java
Calibration Tutorial: Tutorial Here
Concepts:
- Camera calibration
- Lens distortion
- Intrinsic parameters
Relevant Applets:
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* <p>
* Example of how to calibrate a single (monocular) camera using a planar calibration grid. Two types of calibration
* targets can be processed by BoofCV, square grids and chessboard. Square grid is composed of a set of square
* grids and chessboard is a classic chessboard pattern. In general better quality results have been found using
* the chessboard pattern, but parameter tuning is required to achieve optimal performance.
* </p>
*
* <p>
* All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateMonoPlanar}. The code below
* images of calibration targets are loaded and pass in as inputs and the found calibration is saved to an XML file.
* See in code comments for tuning and implementation issues.
* </p>
*
* @see ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleCalibrateMonocularPlanar {
// Detects the target and calibration point inside the target
PlanarCalibrationDetector detector;
// Description of the target's physical dimension
PlanarCalibrationTarget target;
// List of calibration images
List<String> images;
// Most computer images are in a left handed coordinate system. This can cause problems when algorithms
// that assume a right handed coordinate system are used later on. To address this issue the image coordinate
// system is changed to a right handed one if true is passed in for the second parameter.
boolean isLeftHanded;
/**
* Images from Zhang's website. Square grid pattern.
*/
private void setupZhang99() {
// Use the wrapper below for square grid targets.
detector = new WrapPlanarGridTarget(8,8);
// physical description
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridSquare(8, 8, 0.5, 7.0 / 18.0);
// load image list
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/mono/PULNiX_CCD_6mm_Zhang";
images = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory,"CalibIm");
// standard image format
isLeftHanded = true;
}
/**
* Images collected from a Bumblee Bee stereo camera. Large amounts of radial distortion. Chessboard pattern.
*/
private void setupBumbleBee() {
// Use the wrapper below for chessboard targets. The last parameter adjusts the size of the corner detection
// region. TUNE THIS PARAMETER FOR OPTIMAL ACCURACY!
detector = new WrapPlanarChessTarget(3,4,6);
// physical description
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30);
// load image list
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess";
images = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory,"left");
// standard image format
isLeftHanded = true;
}
/**
* Process calibration images, compute intrinsic parameters, save to a file
*/
public void process() {
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm
CalibrateMonoPlanar calibrationAlg = new CalibrateMonoPlanar(detector,isLeftHanded);
// tell it type type of target and which parameters to estimate
calibrationAlg.configure(target, true, 2);
for( String n : images ) {
BufferedImage input = UtilImageIO.loadImage(n);
if( n != null ) {
ImageFloat32 image = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(input,(ImageFloat32)null);
calibrationAlg.addImage(image);
}
}
// process and compute intrinsic parameters
IntrinsicParameters intrinsic = calibrationAlg.process();
// save results to a file and print out
BoofMiscOps.saveXML(intrinsic, "intrinsic.xml");
calibrationAlg.printStatistics();
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---");
System.out.println();
intrinsic.print();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
ExampleCalibrateMonocularPlanar alg = new ExampleCalibrateMonocularPlanar();
// which target should it process
// alg.setupZhang99();
alg.setupBumbleBee();
// compute and save results
alg.process();
}
}