Difference between revisions of "Example Calibrate Planar Stereo"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
(Updated for v0.8) |
||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
</center> | </center> | ||
This example demonstrate how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a high level interface which automatically detects calibration targets in a set of stereo images. After calibration the intrinsic parameters of each camera is found as well as their extrinsic relationship with each other. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below. | |||
Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/master/examples/src/boofcv/examples/ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java] | Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/master/examples/src/boofcv/examples/ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java] | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* Example of how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a planar calibration grid given a set of images. | |||
* Example of how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a planar calibration grid. | * Intrinsic camera parameters are estimated for both cameras individually, then extrinsic parameters | ||
* for the two cameras relative to each other are found This example does not rectify the images, which is | |||
* required for some algorithms. See {@link ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo}. Both square grid and chessboard targets | |||
* are demonstrated in this example. See calibration tutorial for a discussion of different target types and how to | |||
* collect good calibration images. | |||
* | * | ||
* All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateStereoPlanar}. The code below | * All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateStereoPlanar}. The code below | ||
* loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. See in code comments for tuning | * loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. See in code comments for tuning | ||
* and implementation issues. | * and implementation issues. | ||
* | * | ||
* @see ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo | * @see ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo | ||
| Line 62: | Line 59: | ||
List<String> right; | List<String> right; | ||
// | // Many 3D operations assumed a right handed coordinate system with +Z pointing out of the image. | ||
// | // If the image coordinate system is left handed then the y-axis needs to be flipped to meet | ||
boolean | // that requirement. Most of the time this is false. | ||
boolean flipY; | |||
/** | /** | ||
| Line 71: | Line 69: | ||
public void setupBumblebeeSquare() { | public void setupBumblebeeSquare() { | ||
// Use the wrapper below for square grid targets. | // Use the wrapper below for square grid targets. | ||
detector = | detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorSquareGrid(3,4); | ||
// Target physical description | // Target physical description | ||
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridSquare(3, 4, 30,30); | target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridSquare(3, 4, 30,30); | ||
| Line 80: | Line 78: | ||
right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right"); | right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right"); | ||
flipY = false; | |||
} | } | ||
| Line 89: | Line 87: | ||
// Use the wrapper below for chessboard targets. The last parameter adjusts the size of the corner detection | // Use the wrapper below for chessboard targets. The last parameter adjusts the size of the corner detection | ||
// region. TUNE THIS PARAMETER FOR OPTIMAL ACCURACY! | // region. TUNE THIS PARAMETER FOR OPTIMAL ACCURACY! | ||
detector = | detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorChessboard(3, 4, 6); | ||
// Target physical description | // Target physical description | ||
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30); | target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30); | ||
| Line 98: | Line 96: | ||
right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right"); | right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right"); | ||
flipY = false; | |||
} | } | ||
| Line 106: | Line 104: | ||
public void process() { | public void process() { | ||
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm | // Declare and setup the calibration algorithm | ||
CalibrateStereoPlanar calibratorAlg = new CalibrateStereoPlanar(detector, | CalibrateStereoPlanar calibratorAlg = new CalibrateStereoPlanar(detector, flipY); | ||
calibratorAlg.configure(target, | calibratorAlg.configure(target, true, 2); | ||
// ensure the lists are in the same order | // ensure the lists are in the same order | ||
Revision as of 06:44, 12 May 2012
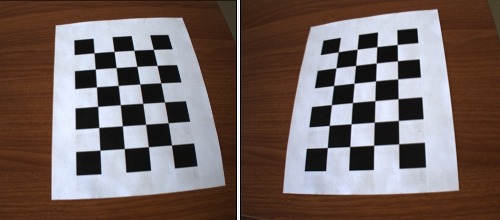
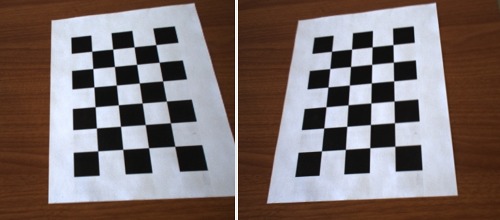
Stereo Camera Calibration with Planar Targets
This example demonstrate how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a high level interface which automatically detects calibration targets in a set of stereo images. After calibration the intrinsic parameters of each camera is found as well as their extrinsic relationship with each other. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below.
Example File: ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java
Calibration Tutorial: Wikipage
Concepts:
- Camera calibration
- Lens distortion
- Intrinsic parameters
- Stereo Vision
Relevant Applets:
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Example of how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a planar calibration grid given a set of images.
* Intrinsic camera parameters are estimated for both cameras individually, then extrinsic parameters
* for the two cameras relative to each other are found This example does not rectify the images, which is
* required for some algorithms. See {@link ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo}. Both square grid and chessboard targets
* are demonstrated in this example. See calibration tutorial for a discussion of different target types and how to
* collect good calibration images.
*
* All the image processing and calibration is taken care of inside of {@link CalibrateStereoPlanar}. The code below
* loads calibration images as inputs, calibrates, and saves results to an XML file. See in code comments for tuning
* and implementation issues.
*
* @see ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo
* @see CalibrateStereoPlanar
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar {
// Detects the target and calibration point inside the target
PlanarCalibrationDetector detector;
// Description of the target's physical dimension
PlanarCalibrationTarget target;
// List of calibration images
List<String> left;
List<String> right;
// Many 3D operations assumed a right handed coordinate system with +Z pointing out of the image.
// If the image coordinate system is left handed then the y-axis needs to be flipped to meet
// that requirement. Most of the time this is false.
boolean flipY;
/**
* Square grid target taken by a PtGrey Bumblebee camera.
*/
public void setupBumblebeeSquare() {
// Use the wrapper below for square grid targets.
detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorSquareGrid(3,4);
// Target physical description
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridSquare(3, 4, 30,30);
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Square";
left = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "left");
right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right");
flipY = false;
}
/**
* Chessboard target taken by a PtGrey Bumblebee camera.
*/
public void setupBumblebeeChess() {
// Use the wrapper below for chessboard targets. The last parameter adjusts the size of the corner detection
// region. TUNE THIS PARAMETER FOR OPTIMAL ACCURACY!
detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorChessboard(3, 4, 6);
// Target physical description
target = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30);
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess";
left = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "left");
right = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory, "right");
flipY = false;
}
/**
* Process calibration images, compute intrinsic parameters, save to a file
*/
public void process() {
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm
CalibrateStereoPlanar calibratorAlg = new CalibrateStereoPlanar(detector, flipY);
calibratorAlg.configure(target, true, 2);
// ensure the lists are in the same order
Collections.sort(left);
Collections.sort(right);
for( int i = 0; i < left.size(); i++ ) {
BufferedImage l = UtilImageIO.loadImage(left.get(i));
BufferedImage r = UtilImageIO.loadImage(right.get(i));
ImageFloat32 imageLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(l,(ImageFloat32)null);
ImageFloat32 imageRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(r,(ImageFloat32)null);
calibratorAlg.addPair(imageLeft, imageRight);
}
// Process and compute calibration parameters
StereoParameters stereoCalib = calibratorAlg.process();
// save results to a file and print out
BoofMiscOps.saveXML(stereoCalib, "stereo.xml");
stereoCalib.print();
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar alg = new ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar();
// Select which set of targets to use
alg.setupBumblebeeChess();
// alg.setupBumblebeeSquare();
// compute and save results
alg.process();
}
}