Difference between revisions of "Example Calibrate Planar Stereo"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to search (Updated for v0.8) |
m |
||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* Example of how to calibrate a | * Example of how to calibrate a single (monocular) camera given a set of observed calibration. | ||
* | * points using the Zhang99 algorithm. Unlike in the other examples, the image processing has | ||
* not already been done. In theory you could add your own more exotic targets by writing | |||
* | * custom code to detect the target, which is left as an exercise for the reader. For example, | ||
* | * have multiple targets visible or calibrate using circles. | ||
* | |||
* | * | ||
* @author Peter Abeles | * @author Peter Abeles | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public class | public class ExampleCalibrateMonocularPoints { | ||
/ | /** | ||
* Given a description of the calibration target and the observed location of the calibration | |||
* | |||
* @param targetDesc Describes the target's known physical structure | |||
* @param observations Observations of the target in different images | |||
*/ | |||
public static void calibrate( PlanarCalibrationTarget targetDesc , | |||
List<List<Point2D_F64>> observations ) { | |||
// Assume zero skew and model lens distortion with two radial parameters | |||
CalibrationPlanarGridZhang99 zhang99 = | |||
new CalibrationPlanarGridZhang99(targetDesc,true,2); | |||
if( !zhang99.process(observations) ) | |||
throw new RuntimeException("Calibration failed!"); | |||
// Get camera parameters and extrinsic target location in each image | |||
Zhang99Parameters found = zhang99.getOptimized(); | |||
// Convenient function for converting from specialized Zhang99 format to generalized | |||
IntrinsicParameters param = found.convertToIntrinsic(); | |||
// print the results to standard out | |||
param.print(); | |||
// save to a file using XML | |||
BoofMiscOps.saveXML(param,"intrinsic.xml"); | |||
} | } | ||
/** | /** | ||
* | * Detects calibration points found in several images and returned as a list. Not the focus of this example. | ||
*/ | */ | ||
public | public static List<List<Point2D_F64>> loadObservations() { | ||
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"; | String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess"; | ||
List<String> imageNames = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory,"left"); | |||
PlanarCalibrationDetector detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorChessboard(3, 4, 6); | |||
List<List<Point2D_F64>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Point2D_F64>>(); | |||
for( String n : imageNames ) { | |||
BufferedImage img = UtilImageIO.loadImage(n); | |||
ImageFloat32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(img,(ImageFloat32)null); | |||
if( !detector.process(input) ) | |||
throw new RuntimeException("Detection failed!"); | |||
ret.add(detector.getPoints()); | |||
} | } | ||
return ret; | |||
} | } | ||
public static void main( String args[] ) { | public static void main( String args[] ) { | ||
// target description and list of observations | |||
PlanarCalibrationTarget desc = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30); | |||
// | List<List<Point2D_F64>> calibPts = loadObservations(); | ||
// | // Calibrate the camera | ||
calibrate(desc,calibPts); | |||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Revision as of 15:45, 6 November 2012
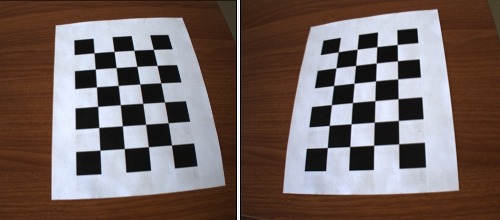
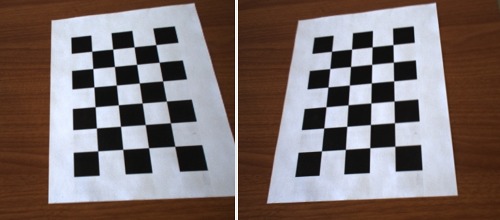
Stereo Camera Calibration with Planar Targets
This example demonstrate how to calibrate a stereo camera system using a high level interface which automatically detects calibration targets in a set of stereo images. After calibration the intrinsic parameters of each camera is found as well as their extrinsic relationship with each other. Both the square grid and chessboard patterns are supported by this example. For a full description of the calibration process and instruction on how to do it yourself see the tutorial linked to below.
Example File: ExampleCalibrateStereoPlanar.java
Calibration Tutorial: Wikipage
Concepts:
- Camera calibration
- Lens distortion
- Intrinsic parameters
- Stereo Vision
Relevant Applets:
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Example of how to calibrate a single (monocular) camera given a set of observed calibration.
* points using the Zhang99 algorithm. Unlike in the other examples, the image processing has
* not already been done. In theory you could add your own more exotic targets by writing
* custom code to detect the target, which is left as an exercise for the reader. For example,
* have multiple targets visible or calibrate using circles.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleCalibrateMonocularPoints {
/**
* Given a description of the calibration target and the observed location of the calibration
*
* @param targetDesc Describes the target's known physical structure
* @param observations Observations of the target in different images
*/
public static void calibrate( PlanarCalibrationTarget targetDesc ,
List<List<Point2D_F64>> observations ) {
// Assume zero skew and model lens distortion with two radial parameters
CalibrationPlanarGridZhang99 zhang99 =
new CalibrationPlanarGridZhang99(targetDesc,true,2);
if( !zhang99.process(observations) )
throw new RuntimeException("Calibration failed!");
// Get camera parameters and extrinsic target location in each image
Zhang99Parameters found = zhang99.getOptimized();
// Convenient function for converting from specialized Zhang99 format to generalized
IntrinsicParameters param = found.convertToIntrinsic();
// print the results to standard out
param.print();
// save to a file using XML
BoofMiscOps.saveXML(param,"intrinsic.xml");
}
/**
* Detects calibration points found in several images and returned as a list. Not the focus of this example.
*/
public static List<List<Point2D_F64>> loadObservations() {
String directory = "../data/evaluation/calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess";
List<String> imageNames = BoofMiscOps.directoryList(directory,"left");
PlanarCalibrationDetector detector = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.detectorChessboard(3, 4, 6);
List<List<Point2D_F64>> ret = new ArrayList<List<Point2D_F64>>();
for( String n : imageNames ) {
BufferedImage img = UtilImageIO.loadImage(n);
ImageFloat32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(img,(ImageFloat32)null);
if( !detector.process(input) )
throw new RuntimeException("Detection failed!");
ret.add(detector.getPoints());
}
return ret;
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// target description and list of observations
PlanarCalibrationTarget desc = FactoryPlanarCalibrationTarget.gridChess(3, 4, 30);
List<List<Point2D_F64>> calibPts = loadObservations();
// Calibrate the camera
calibrate(desc,calibPts);
}
}