Difference between revisions of "Example Binary Image"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
|||
| Line 62: | Line 62: | ||
binary = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(binary, null); | binary = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(binary, null); | ||
// | // Detect blobs inside the binary image and assign labels to them | ||
int numBlobs = BinaryImageOps.labelBlobs4(binary,blobs); | int numBlobs = BinaryImageOps.labelBlobs4(binary,blobs); | ||
Revision as of 10:51, 18 October 2011
Binary Image Processing
Binary images are images where each pixel can take on two values, typically represented by 0 or 1. Binary images are easy to compute and fast to process, which makes them popular in many applications.
Example File: BinaryImageExample.java
Concepts:
- Image Thresholding
- Morphological Operations
- Binary Labeling
- Pixel Math
- Image Rendering
Basic Example
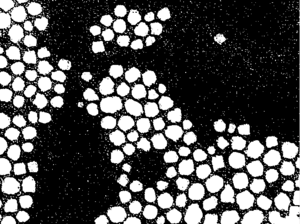
In this example a threshold is computed for the input image dynamically and the resulting binary image shown.
public static void binaryExample( BufferedImage image )
{
// convert into a usable format
ImageFloat32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(image,null,ImageFloat32.class);
ImageUInt8 binary = new ImageUInt8(input.width,input.height);
// the mean pixel value is often a reasonable threshold when creating a binary image
float mean = PixelMath.sum(input)/(input.width*input.height);
// create a binary image
ThresholdImageOps.threshold(input,binary,mean,true);
// Render the binary image for output and display it in a window
BufferedImage visualBinary = VisualizeBinaryData.renderBinary(binary,null);
ShowImages.showWindow(visualBinary,"Binary Image");
}
Labeled Example
Here clustered of blobs are detected and arbitrarily assigned labels.
public static void labeledExample( BufferedImage image )
{
// convert into a usable format
ImageFloat32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(image,null,ImageFloat32.class);
ImageUInt8 binary = new ImageUInt8(input.width,input.height);
ImageSInt32 blobs = new ImageSInt32(input.width,input.height);
// the mean pixel value is often a reasonable threshold when creating a binary image
float mean = PixelMath.sum(input)/(input.width*input.height);
// create a binary image
ThresholdImageOps.threshold(input,binary,mean,true);
// remove small blobs through erosion and dilation
// The null in the input indicates that it should internally declare the work image it needs
// this is less efficient, but easier to code.
binary = BinaryImageOps.erode8(binary,null);
binary = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(binary, null);
// Detect blobs inside the binary image and assign labels to them
int numBlobs = BinaryImageOps.labelBlobs4(binary,blobs);
// Render the binary image for output and display it in a window
BufferedImage visualized = VisualizeBinaryData.renderLabeled(blobs, numBlobs, null);
ShowImages.showWindow(visualized,"Labeled Image");
}