Difference between revisions of "Example Three View Stereo Uncalibrated"
From BoofCV
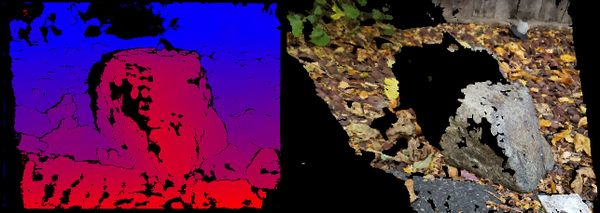
Jump to navigationJump to search (Created page with " thumb|center|600px|Left is disparity image and Right is found 3D Point Cloud Given three views from an unknown camera comp...") |
m |
||
| Line 14: | Line 14: | ||
* Projective Geometry | * Projective Geometry | ||
* Metric Geometry | * Metric Geometry | ||
* | * Bundle Adjustment | ||
* Three View Feature Association | |||
* Trifocal Tensor | |||
* Rectification | * Rectification | ||
* Dense stereo processing | * Dense stereo processing | ||
| Line 20: | Line 22: | ||
Related Tutorials/Example Code: | Related Tutorials/Example Code: | ||
* [[Example_Stereo_Single_Camera| Stereo Single Calibrated Camera]] | * [[Example_Stereo_Single_Camera| Stereo Single Calibrated Camera]] | ||
* [[Example_Stereo_Uncalibrated| Stereo Uncalibrated]] | |||
* [[Example_Sparse_Bundle_Adjustment| Bundle Adjustment]] | |||
* [[Example_Stereo_Disparity| Stereo Disparity Example]] | * [[Example_Stereo_Disparity| Stereo Disparity Example]] | ||
* [[Example_Rectification_Calibrated| Calibrated Stereo Rectification Example]] | * [[Example_Rectification_Calibrated| Calibrated Stereo Rectification Example]] | ||
Revision as of 21:09, 26 December 2018
Given three views from an unknown camera compute a dense 3D point cloud. Similar to the uncalibrated two view example, but much more stable. With three view's its possible to prune many more false associations because there is a unique projection in each view. A Trifocal Tensor fit to the associations with RANSAC instead of a Fundamental matrix in the two view case.
See code comments below for a summary of all the processing steps involved.
Example File:
Concepts:
- Self calibration / Automatic Calibration
- Projective Geometry
- Metric Geometry
- Bundle Adjustment
- Three View Feature Association
- Trifocal Tensor
- Rectification
- Dense stereo processing
Related Tutorials/Example Code:
- Stereo Single Calibrated Camera
- Stereo Uncalibrated
- Bundle Adjustment
- Stereo Disparity Example
- Calibrated Stereo Rectification Example
- Camera Calibration Tutorial
Example Code
/**
* In this example three uncalibrated images are used to compute a point cloud. Extrinsic as well as all intrinsic
* parameters (e.g. focal length and lens distortion) are found. Stereo disparity is computed between two of
* the three views and the point cloud derived from that. To keep the code (relatively) simple, extra steps which
* improve convergence have been omitted. See {@link boofcv.alg.sfm.structure.ThreeViewEstimateMetricScene} for
* a more robust version of what has been presented here. Even with these simplifications this example can be
* difficult to fully understand.
*
* Three images produce a more stable "practical" algorithm when dealing with uncalibrated images.
* With just two views its impossible to remove all false matches since an image feature can lie any where
* along an epipolar line in other other view. Even with three views, results are not always stable or 100% accurate
* due to scene geometry and here the views were captured. In general you want a well textured scene with objects
* up close and far away, and images taken with translational
* motion. Pure rotation and planar scenes are impossible to estimate the structure from.
*
* Steps:
* <ol>
* <li>Feature Detection (e.g. SURF)</li>
* <li>Two view association</li>
* <li>Find 3 View Tracks</li>
* <li>Fit Trifocal tensor using RANSAC</li>
* <li>Get and refine camera matrices</li>
* <li>Compute dual absolute quadratic</li>
* <li>Estimate intrinsic parameters from DAC</li>
* <li>Estimate metric scene structure</li>
* <li>Sparse bundle adjustment</li>
* <li>Rectify two of the images</li>
* <li>Compute stereo disparity</li>
* <li>Convert into a point cloud</li>
* </ol>
*
* For a more stable and accurate version this example see {@link ThreeViewEstimateMetricScene}.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleTrifocalStereoUncalibrated {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String name = "rock_leaves_";
// String name = "mono_wall_";
// String name = "minecraft_cave1_";
// String name = "minecraft_distant_";
// String name = "bobcats_";
// String name = "chicken_";
// String name = "turkey_";
// String name = "rockview_";
// String name = "pebbles_";
// String name = "books_";
// String name = "skull_";
// String name = "triflowers_";
BufferedImage buff01 = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("triple/"+name+"01.jpg"));
BufferedImage buff02 = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("triple/"+name+"02.jpg"));
BufferedImage buff03 = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("triple/"+name+"03.jpg"));
Planar<GrayU8> color01 = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(buff01,true,ImageType.pl(3,GrayU8.class));
Planar<GrayU8> color02 = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(buff02,true,ImageType.pl(3,GrayU8.class));
Planar<GrayU8> color03 = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(buff03,true,ImageType.pl(3,GrayU8.class));
GrayU8 image01 = ConvertImage.average(color01,null);
GrayU8 image02 = ConvertImage.average(color02,null);
GrayU8 image03 = ConvertImage.average(color03,null);
// using SURF features. Robust and fairly fast to compute
DetectDescribePoint<GrayU8,BrightFeature> detDesc = FactoryDetectDescribe.surfStable(
new ConfigFastHessian(0, 4, 1000, 1, 9, 4, 2), null,null, GrayU8.class);
FastQueue<Point2D_F64> locations01 = new FastQueue<>(Point2D_F64.class,true);
FastQueue<Point2D_F64> locations02 = new FastQueue<>(Point2D_F64.class,true);
FastQueue<Point2D_F64> locations03 = new FastQueue<>(Point2D_F64.class,true);
FastQueue<BrightFeature> features01 = UtilFeature.createQueue(detDesc,100);
FastQueue<BrightFeature> features02 = UtilFeature.createQueue(detDesc,100);
FastQueue<BrightFeature> features03 = UtilFeature.createQueue(detDesc,100);
// Converting data formats for the found features into what can be processed by SFM algorithms
// Notice how the image center is subtracted from the coordinates? In many cases a principle point
// of zero is assumed. This is a reasonable assumption in almost all modern cameras. Errors in
// the principle point tend to materialize as translations and are non fatal.
int width = image01.width, height = image01.height;
System.out.println("Image Shape "+width+" x "+height);
double cx = width/2;
double cy = height/2;
detDesc.detect(image01);
for (int i = 0; i < detDesc.getNumberOfFeatures(); i++) {
Point2D_F64 pixel = detDesc.getLocation(i);
locations01.grow().set(pixel.x-cx,pixel.y-cy);
features01.grow().setTo(detDesc.getDescription(i));
}
detDesc.detect(image02);
for (int i = 0; i < detDesc.getNumberOfFeatures(); i++) {
Point2D_F64 pixel = detDesc.getLocation(i);
locations02.grow().set(pixel.x-cx,pixel.y-cy);
features02.grow().setTo(detDesc.getDescription(i));
}
detDesc.detect(image03);
for (int i = 0; i < detDesc.getNumberOfFeatures(); i++) {
Point2D_F64 pixel = detDesc.getLocation(i);
locations03.grow().set(pixel.x-cx,pixel.y-cy);
features03.grow().setTo(detDesc.getDescription(i));
}
System.out.println("features01.size = "+features01.size);
System.out.println("features02.size = "+features02.size);
System.out.println("features03.size = "+features03.size);
ScoreAssociation<BrightFeature> scorer = FactoryAssociation.scoreEuclidean(BrightFeature.class,true);
AssociateDescription<BrightFeature> associate = FactoryAssociation.greedy(scorer, 0.1, true);
AssociateThreeByPairs<BrightFeature> associateThree = new AssociateThreeByPairs<>(associate,BrightFeature.class);
associateThree.setFeaturesA(features01);
associateThree.setFeaturesB(features02);
associateThree.setFeaturesC(features03);
associateThree.associate();
System.out.println("Total Matched Triples = "+associateThree.getMatches().size);
ConfigRansac configRansac = new ConfigRansac();
configRansac.maxIterations = 500;
configRansac.inlierThreshold = 1;
ConfigTrifocal configTri = new ConfigTrifocal();
ConfigTrifocalError configError = new ConfigTrifocalError();
configError.model = ConfigTrifocalError.Model.REPROJECTION_REFINE;
Ransac<TrifocalTensor,AssociatedTriple> ransac =
FactoryMultiViewRobust.trifocalRansac(configTri,configError,configRansac);
FastQueue<AssociatedTripleIndex> associatedIdx = associateThree.getMatches();
FastQueue<AssociatedTriple> associated = new FastQueue<>(AssociatedTriple.class,true);
for (int i = 0; i < associatedIdx.size; i++) {
AssociatedTripleIndex p = associatedIdx.get(i);
associated.grow().set(locations01.get(p.a),locations02.get(p.b),locations03.get(p.c));
}
ransac.process(associated.toList());
List<AssociatedTriple> inliers = ransac.getMatchSet();
TrifocalTensor model = ransac.getModelParameters();
System.out.println("Remaining after RANSAC "+inliers.size());
// Show remaining associations from RANSAC
AssociatedTriplePanel triplePanel = new AssociatedTriplePanel();
triplePanel.setPixelOffset(cx,cy);
triplePanel.setImages(buff01,buff02,buff03);
triplePanel.setAssociation(inliers);
ShowImages.showWindow(triplePanel,"Associations", true);
// estimate using all the inliers
// No need to re-scale the input because the estimator automatically adjusts the input on its own
configTri.which = EnumTrifocal.ALGEBRAIC_7;
configTri.converge.maxIterations = 100;
Estimate1ofTrifocalTensor trifocalEstimator = FactoryMultiView.trifocal_1(configTri);
if( !trifocalEstimator.process(inliers,model) )
throw new RuntimeException("Estimator failed");
model.print();
DMatrixRMaj P1 = CommonOps_DDRM.identity(3,4);
DMatrixRMaj P2 = new DMatrixRMaj(3,4);
DMatrixRMaj P3 = new DMatrixRMaj(3,4);
MultiViewOps.extractCameraMatrices(model,P2,P3);
// Most of the time this refinement step makes little difference, but in some edges cases it appears
// to help convergence
System.out.println("Refining projective camera matrices");
RefineThreeViewProjective refineP23 = FactoryMultiView.threeViewRefine(null);
if( !refineP23.process(inliers,P2,P3,P2,P3) )
throw new RuntimeException("Can't refine P2 and P3!");
SelfCalibrationLinearDualQuadratic selfcalib = new SelfCalibrationLinearDualQuadratic(1.0);
selfcalib.addCameraMatrix(P1);
selfcalib.addCameraMatrix(P2);
selfcalib.addCameraMatrix(P3);
List<CameraPinhole> listPinhole = new ArrayList<>();
GeometricResult result = selfcalib.solve();
if(GeometricResult.SOLVE_FAILED != result) {
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
Intrinsic c = selfcalib.getSolutions().get(i);
CameraPinhole p = new CameraPinhole(c.fx,c.fy,0,0,0,width,height);
listPinhole.add(p);
}
} else {
System.out.println("Self calibration failed!");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
CameraPinhole p = new CameraPinhole(width/2,width/2,0,0,0,width,height);
listPinhole.add(p);
}
}
// print the initial guess for focal length. Focal length is a crtical and difficult to estimate
// parameter
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
CameraPinhole r = listPinhole.get(i);
System.out.println("fx="+r.fx+" fy="+r.fy+" skew="+r.skew);
}
System.out.println("Projective to metric");
// convert camera matrix from projective to metric
DMatrixRMaj H = new DMatrixRMaj(4,4); // storage for rectifying homography
if( !MultiViewOps.absoluteQuadraticToH(selfcalib.getQ(),H) )
throw new RuntimeException("Projective to metric failed");
DMatrixRMaj K = new DMatrixRMaj(3,3);
List<Se3_F64> worldToView = new ArrayList<>();
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
worldToView.add( new Se3_F64());
}
// ignore K since we already have that
MultiViewOps.projectiveToMetric(P1,H,worldToView.get(0),K);
MultiViewOps.projectiveToMetric(P2,H,worldToView.get(1),K);
MultiViewOps.projectiveToMetric(P3,H,worldToView.get(2),K);
// scale is arbitrary. Set max translation to 1
adjustTranslationScale(worldToView);
// Construct bundle adjustment data structure
SceneStructureMetric structure = new SceneStructureMetric(false);
SceneObservations observations = new SceneObservations(3);
structure.initialize(3,3,inliers.size());
for (int i = 0; i < listPinhole.size(); i++) {
BundlePinholeSimplified bp = new BundlePinholeSimplified();
bp.f = listPinhole.get(i).fx;
structure.setCamera(i,false,bp);
structure.setView(i,i==0,worldToView.get(i));
structure.connectViewToCamera(i,i);
}
for (int i = 0; i < inliers.size(); i++) {
AssociatedTriple t = inliers.get(i);
observations.getView(0).add(i,(float)t.p1.x,(float)t.p1.y);
observations.getView(1).add(i,(float)t.p2.x,(float)t.p2.y);
observations.getView(2).add(i,(float)t.p3.x,(float)t.p3.y);
structure.connectPointToView(i,0);
structure.connectPointToView(i,1);
structure.connectPointToView(i,2);
}
// Initial estimate for point 3D locations
triangulatePoints(structure,observations);
ConfigLevenbergMarquardt configLM = new ConfigLevenbergMarquardt();
configLM.dampeningInitial = 1e-3;
configLM.hessianScaling = false;
ConfigBundleAdjustment configSBA = new ConfigBundleAdjustment();
configSBA.configOptimizer = configLM;
// Create and configure the bundle adjustment solver
BundleAdjustment<SceneStructureMetric> bundleAdjustment = FactoryMultiView.bundleAdjustmentMetric(configSBA);
// prints out useful debugging information that lets you know how well it's converging
// bundleAdjustment.setVerbose(System.out,0);
bundleAdjustment.configure(1e-6, 1e-6, 100); // convergence criteria
bundleAdjustment.setParameters(structure,observations);
bundleAdjustment.optimize(structure);
// See if the solution is physically possible. If not fix and run bundle adjustment again
checkBehindCamera(structure, observations, bundleAdjustment);
// It's very difficult to find the best solution due to the number of local minimum. In the three view
// case it's often the problem that a small translation is virtually identical to a small rotation.
// Convergence can be improved by considering that possibility
// Now that we have a decent solution, prune the worst outliers to improve the fit quality even more
PruneStructureFromSceneMetric pruner = new PruneStructureFromSceneMetric(structure,observations);
pruner.pruneObservationsByErrorRank(0.7);
pruner.pruneViews(10);
pruner.prunePoints(1);
bundleAdjustment.setParameters(structure,observations);
bundleAdjustment.optimize(structure);
System.out.println("Final Views");
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
BundlePinholeSimplified cp = structure.getCameras()[i].getModel();
Vector3D_F64 T = structure.getViews()[i].worldToView.T;
System.out.printf("[ %d ] f = %5.1f T=%s\n",i,cp.f,T.toString());
}
System.out.println("\n\nComputing Stereo Disparity");
BundlePinholeSimplified cp = structure.getCameras()[0].getModel();
CameraPinholeRadial intrinsic01 = new CameraPinholeRadial();
intrinsic01.fsetK(cp.f,cp.f,0,cx,cy,width,height);
intrinsic01.fsetRadial(cp.k1,cp.k2);
cp = structure.getCameras()[1].getModel();
CameraPinholeRadial intrinsic02 = new CameraPinholeRadial();
intrinsic02.fsetK(cp.f,cp.f,0,cx,cy,width,height);
intrinsic02.fsetRadial(cp.k1,cp.k2);
Se3_F64 leftToRight = structure.views[1].worldToView;
// TODO dynamic max disparity
computeStereoCloud(image01,image02,color01,color02,intrinsic01,intrinsic02,leftToRight,0,250);
}
private static void adjustTranslationScale(List<Se3_F64> worldToView) {
double maxT = 0;
for( Se3_F64 p : worldToView ) {
maxT = Math.max(maxT,p.T.norm());
}
for( Se3_F64 p : worldToView ) {
p.T.scale(1.0/maxT);
p.print();
}
}
// TODO Do this correction without running bundle adjustment again
private static void checkBehindCamera(SceneStructureMetric structure, SceneObservations observations, BundleAdjustment<SceneStructureMetric> bundleAdjustment) {
int totalBehind = 0;
Point3D_F64 X = new Point3D_F64();
for (int i = 0; i < structure.points.length; i++) {
structure.points[i].get(X);
if( X.z < 0 )
totalBehind++;
}
structure.views[1].worldToView.T.print();
if( totalBehind > structure.points.length/2 ) {
System.out.println("Flipping because it's reversed. score = "+bundleAdjustment.getFitScore());
for (int i = 1; i < structure.views.length; i++) {
Se3_F64 w2v = structure.views[i].worldToView;
w2v.set(w2v.invert(null));
}
triangulatePoints(structure,observations);
bundleAdjustment.setParameters(structure,observations);
bundleAdjustment.optimize(structure);
System.out.println(" after = "+bundleAdjustment.getFitScore());
} else {
System.out.println("Points not behind camera. "+totalBehind+" / "+structure.points.length);
}
}
public static void computeStereoCloud( GrayU8 distortedLeft, GrayU8 distortedRight ,
Planar<GrayU8> colorLeft, Planar<GrayU8> colorRight,
CameraPinholeRadial intrinsicLeft ,
CameraPinholeRadial intrinsicRight ,
Se3_F64 leftToRight ,
int minDisparity , int maxDisparity) {
// drawInliers(origLeft, origRight, intrinsic, inliers);
int width = distortedLeft.width;
int height = distortedRight.height;
// Rectify and remove lens distortion for stereo processing
DMatrixRMaj rectifiedK = new DMatrixRMaj(3, 3);
DMatrixRMaj rectifiedR = new DMatrixRMaj(3, 3);
// rectify a colored image
Planar<GrayU8> rectColorLeft = colorLeft.createSameShape();
Planar<GrayU8> rectColorRight = colorLeft.createSameShape();
GrayU8 rectMask = new GrayU8(colorLeft.width,colorLeft.height);
rectifyImages(colorLeft, colorRight, leftToRight, intrinsicLeft,intrinsicRight,
rectColorLeft, rectColorRight,rectMask, rectifiedK,rectifiedR);
if(rectifiedK.get(0,0) < 0)
throw new RuntimeException("Egads");
System.out.println("Rectified K");
rectifiedK.print();
System.out.println("Rectified R");
rectifiedR.print();
GrayU8 rectifiedLeft = distortedLeft.createSameShape();
GrayU8 rectifiedRight = distortedRight.createSameShape();
ConvertImage.average(rectColorLeft,rectifiedLeft);
ConvertImage.average(rectColorRight,rectifiedRight);
// compute disparity
StereoDisparity<GrayS16, GrayF32> disparityAlg =
FactoryStereoDisparity.regionSubpixelWta(DisparityAlgorithms.RECT_FIVE,
minDisparity, maxDisparity, 6, 6, 30, 3, 0.05, GrayS16.class);
// Apply the Laplacian across the image to add extra resistance to changes in lighting or camera gain
GrayS16 derivLeft = new GrayS16(width,height);
GrayS16 derivRight = new GrayS16(width,height);
LaplacianEdge.process(rectifiedLeft, derivLeft);
LaplacianEdge.process(rectifiedRight,derivRight);
// process and return the results
disparityAlg.process(derivLeft, derivRight);
GrayF32 disparity = disparityAlg.getDisparity();
RectifyImageOps.applyMask(disparity,rectMask,0);
// show results
BufferedImage visualized = VisualizeImageData.disparity(disparity, null, minDisparity, maxDisparity, 0);
BufferedImage outLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectColorLeft, new BufferedImage(width,height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB),true);
BufferedImage outRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectColorRight, new BufferedImage(width,height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB),true);
ShowImages.showWindow(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, outLeft, outRight), "Rectification",true);
ShowImages.showWindow(visualized, "Disparity",true);
showPointCloud(disparity, outLeft, leftToRight, rectifiedK,rectifiedR, minDisparity, maxDisparity);
}
}