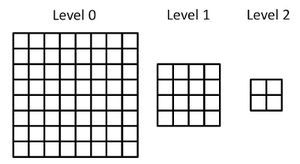
Example Image Pyramid
Image pyramids are a common way to represent multi-resolution image information. In an image pyramid, upper layers are lower resolution versions of the lower layers. BoofCV provides two types of image pyramids built in; PyramidDiscrete and PyramidFloat. PyramidDiscrete only allows the ratio between adjacent to have positive integer values, while PyramidFloat allows any arbitrary positive value. Discrete pyramids are much faster than float pyramids, but much more restrictive.
Inside of BoofCV several algorithms make use of these two types of pyramids. The KLT feature tracker uses a discrete pyramid and is the fastest feature tracker. Pyramid based scale space feature detectors use the float pyramid.
Two code examples are provided below which demonstrate how to construct and visualize each type of pyramid.
Example Code:
Concepts:
- Multi-resolution image processing
- Discrete Vs. Float pyramids
- Image scaling
Image Pyramid Discrete
/**
* Demonstrates how to construct and display a {@link PyramidDiscrete}. Discrete pyramids require that
* each level has a relative scale with an integer ratio and is updated by sparsely sub-sampling. These
* restrictions allows a very quick update across scale space.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExamplePyramidDiscrete<T extends ImageGray<T>> {
// specifies the image type
Class<T> imageType;
// The pyramid data structure
PyramidDiscrete<T> pyramid;
public ExamplePyramidDiscrete(Class<T> imageType) {
this.imageType = imageType;
}
/**
* Creates a fairly standard pyramid and updater.
*/
public void standard() {
// Each level in the pyramid must have a ratio with the previously layer that is an integer value
pyramid = FactoryPyramid.discreteGaussian(new int[]{1,2,4,8},-1,2,true, ImageType.single(imageType));
}
/**
* Creates a more unusual pyramid and updater.
*/
public void unusual() {
// Note that the first level does not have to be one
pyramid = FactoryPyramid.discreteGaussian(new int[]{2,6},-1,2,true, ImageType.single(imageType));
// Other kernels can also be used besides Gaussian
Kernel1D kernel;
if(GeneralizedImageOps.isFloatingPoint(imageType) ) {
kernel = FactoryKernel.table1D_F32(2,true);
} else {
kernel = FactoryKernel.table1D_S32(2);
}
}
/**
* Updates and displays the pyramid.
*/
public void process( BufferedImage image ) {
T input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromSingle(image, null, imageType);
pyramid.process(input);
DiscretePyramidPanel gui = new DiscretePyramidPanel();
gui.setPyramid(pyramid);
gui.render();
ShowImages.showWindow(gui,"Image Pyramid");
// To get an image at any of the scales simply call this get function
T imageAtScale = pyramid.getLayer(1);
ShowImages.showWindow(ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(imageAtScale,null,true),"Image at layer 1");
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("standard/barbara.jpg"));
ExamplePyramidDiscrete<GrayF32> app = new ExamplePyramidDiscrete<>(GrayF32.class);
// ExamplePyramidDiscrete<GrayU8> app = new ExamplePyramidDiscrete<>(GrayU8.class);
app.standard();
// app.unusual();
app.process(image);
}
}
Image Pyramid Float
/**
* Demonstrates how to construct and display a {@link PyramidFloat}. Float pyramids require only require
* that each layer's scale be larger than the scale of the previous layer. Interpolation is used to allow
* sub-sampling at arbitrary scales. All of this additional flexibility comes at the cost of speed
* when compared to a {@link PyramidDiscrete}.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExamplePyramidFloat<T extends ImageGray<T>> {
// specifies the image type
Class<T> imageType;
// The pyramid data structure
PyramidFloat<T> pyramid;
public ExamplePyramidFloat(Class<T> imageType) {
this.imageType = imageType;
}
/**
* Creates a fairly standard pyramid and updater.
*/
public void standard() {
// Scale factory for each layer can be any floating point value which is larger than
// the previous layer's scale.
double scales[] = new double[]{1,1.5,2,2.5,3,5,8,15};
// the amount of blur which is applied to each layer in the pyramid after the previous layer has been sampled
double sigmas[] = new double[]{1,1,1,1,1,1,1,1};
pyramid = FactoryPyramid.floatGaussian(scales,sigmas,imageType);
}
/**
* Updates and displays the pyramid.
*/
public void process( BufferedImage image ) {
T input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromSingle(image, null, imageType);
pyramid.process(input);
ImagePyramidPanel<T> gui = new ImagePyramidPanel<>();
gui.set(pyramid, true);
gui.render();
ShowImages.showWindow(gui,"Image Pyramid Float");
// To get an image at any of the scales simply call this get function
T imageAtScale = pyramid.getLayer(1);
ShowImages.showWindow(ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(imageAtScale,null,true),"Image at layer 1");
}
public static void main( String[] args ) {
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("standard/barbara.jpg"));
ExamplePyramidFloat<GrayF32> app = new ExamplePyramidFloat<>(GrayF32.class);
// ExamplePyramidFloat<GrayU8> app = new ExamplePyramidFloat<>(GrayU8.class);
app.standard();
app.process(image);
}
}