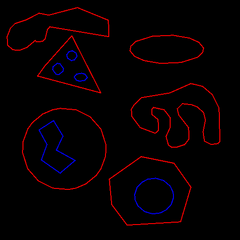
Example Fit Polygon
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to search
Demonstration for how to fit a polygon to object contours and edges. A polygon or line segment sequence can be fit to contours or edges. The contours can be found from binary blobs and the edge sequence from Canny edge detector. This is often a useful preprocessing step before applying a higher level image processing algorithm.
Example Code:
Concepts:
- Object contours/edges
- Shape fitting
Relevant Applets:
Example Code
/**
* Demonstration of how to convert a point sequence describing an objects outline/contour into a sequence of line
* segments. Useful when analysing shapes such as squares and triangles or when trying to simply the low level
* pixel output.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleFitPolygon {
// Polynomial fitting tolerances
static double toleranceDist = 2;
static double toleranceAngle= Math.PI/10;
/**
* Fits a polygons the found contours around binary blobs. This demonstrates how it can be used to handle
* connected loops of points
*/
public static void fitBinaryImage(ImageFloat32 input) {
ImageUInt8 binary = new ImageUInt8(input.width,input.height);
BufferedImage polygon = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// the mean pixel value is often a reasonable threshold when creating a binary image
double mean = ImageStatistics.mean(input);
// create a binary image by thresholding
ThresholdImageOps.threshold(input, binary, (float) mean, true);
// reduce noise with some filtering
ImageUInt8 filtered = BinaryImageOps.erode8(binary,null);
filtered = BinaryImageOps.dilate8(filtered, null);
// Find the contour around the shapes
List<Contour> contours = BinaryImageOps.contour(filtered,8,null);
// Fit a polygon to each shape and draw the results
Graphics2D g2 = polygon.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
for( Contour c : contours ) {
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(c.external,true,
toleranceDist,toleranceAngle,100);
g2.setColor(Color.RED);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
g2.setColor(Color.BLUE);
for( List<Point2D_I32> internal : c.internal ) {
vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(internal,true,toleranceDist,toleranceAngle,100);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
}
}
ShowImages.showWindow(polygon,"Binary Blob Contours");
}
/**
* Fits a sequence of line-segments into a sequence of points found using the Canny edge detector. In this case
* the points are not connected in a loop. The canny detector produces a more complex tree and the fitted
* points can be a bit noisy compared to the others.
*/
public static void fitCannyEdges( ImageFloat32 input ) {
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
// Finds edges inside the image
CannyEdge<ImageFloat32,ImageFloat32> canny =
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, ImageFloat32.class, ImageFloat32.class);
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,null);
List<EdgeContour> contours = canny.getContours();
Graphics2D g2 = displayImage.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
// used to select colors for each line
Random rand = new Random(234);
for( EdgeContour e : contours ) {
g2.setColor(new Color(rand.nextInt()));
for(EdgeSegment s : e.segments ) {
// fit line segments to the point sequence. Note that loop is false
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(s.points,false,
toleranceDist,toleranceAngle,100);
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes, false, g2);
}
}
ShowImages.showWindow(displayImage,"Canny Trace");
}
/**
* Detects contours inside the binary image generated by canny. Only the external contour is relevant. Often
* easier to deal with than working with Canny edges directly.
*/
public static void fitCannyBinary( ImageFloat32 input ) {
BufferedImage displayImage = new BufferedImage(input.width,input.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
ImageUInt8 binary = new ImageUInt8(input.width,input.height);
// Finds edges inside the image
CannyEdge<ImageFloat32,ImageFloat32> canny =
FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, false, true, ImageFloat32.class, ImageFloat32.class);
canny.process(input,0.1f,0.3f,binary);
List<Contour> contours = BinaryImageOps.contour(binary, 8, null);
Graphics2D g2 = displayImage.createGraphics();
g2.setStroke(new BasicStroke(2));
// used to select colors for each line
Random rand = new Random(234);
for( Contour c : contours ) {
List<PointIndex_I32> vertexes = ShapeFittingOps.fitPolygon(c.external,true,
toleranceDist,toleranceAngle,100);
g2.setColor(new Color(rand.nextInt()));
VisualizeShapes.drawPolygon(vertexes,true,g2);
}
ShowImages.showWindow(displayImage,"Canny Contour");
}
public static void main( String args[] ) {
// load and convert the image into a usable format
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImage("../data/applet/shapes02.png");
ImageFloat32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromSingle(image, null, ImageFloat32.class);
ShowImages.showWindow(image,"Original");
fitCannyEdges(input);
fitCannyBinary(input);
fitBinaryImage(input);
}
}