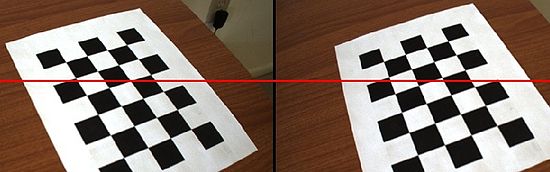
Example Rectification Calibrated
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchStereo rectification is the process of distorting an image such that the epipoles of both images are at infinity. If the epipoles are at infinity along the x-axis, then corresponding features must lie along the same y-coordinates. Using knowledge that correspondence feature's have the same y-coordinate allows for quick searches. Many stereo vision algorithm rely on rectification. The example below demonstrates rectification for a calibrated stereo pair. Note that after calibration the new camera view has a different set of intrinsic parameters.
Example File: ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo.java
Concepts:
- Stereo Rectification
- Stereo Vision
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Shows how to rectify a pair of stereo images with known intrinsic parameters and stereo baseline. When you
* rectify a stereo pair you are applying a transform that removes lens distortion and "rotates" the views
* such that they are parallel to each other, facilitating stereo processing.
*
* The example code does the following:
* <lo>
* <li>Load stereo extrinsic and intrinsic parameters from a file along with a pair of images.</li>
* <li>Undistort and rectify images. This provides one rectification matrix for each image along with a new
* camera calibration matrix.</li>
* <li>The original rectification does not try to maximize view area, however it can be adjusted.</li>
* <li>After rectification is finished the results are displayed.</li>
* </lo>
*
* Note that the y-axis in left and right images align after rectification. You can click in the images to draw a line
* that makes this easy to see. The curved image birder is an artifact of lens distortion being removed.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleRectifyCalibratedStereo {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
String dir = UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/stereo/Bumblebee2_Chess/");
StereoParameters param = CalibrationIO.load(new File(dir, "stereo.yaml"));
// load images
BufferedImage origLeft = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "left05.jpg");
BufferedImage origRight = UtilImageIO.loadImage(dir, "right05.jpg");
// distorted images
Planar<GrayF32> distLeft =
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origLeft, null, true, GrayF32.class);
Planar<GrayF32> distRight =
ConvertBufferedImage.convertFromPlanar(origRight, null, true, GrayF32.class);
// storage for undistorted + rectified images
Planar<GrayF32> rectLeft = distLeft.createSameShape();
Planar<GrayF32> rectRight = distRight.createSameShape();
// Compute rectification
RectifyCalibrated rectifyAlg = RectifyImageOps.createCalibrated();
Se3_F64 leftToRight = param.getRightToLeft().invert(null);
// original camera calibration matrices
DMatrixRMaj K1 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getLeft(), (DMatrixRMaj)null);
DMatrixRMaj K2 = PerspectiveOps.pinholeToMatrix(param.getRight(), (DMatrixRMaj)null);
rectifyAlg.process(K1, new Se3_F64(), K2, leftToRight);
// rectification matrix for each image
DMatrixRMaj rect1 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels1();
DMatrixRMaj rect2 = rectifyAlg.getUndistToRectPixels2();
// New calibration matrix,
// Both cameras have the same one after rectification.
DMatrixRMaj rectK = rectifyAlg.getCalibrationMatrix();
// Adjust the rectification to make the view area more useful
RectifyImageOps.fullViewLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null);
// RectifyImageOps.allInsideLeft(param.left, rect1, rect2, rectK, null);
// undistorted and rectify images
FMatrixRMaj rect1_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3); // TODO simplify code some how
FMatrixRMaj rect2_F32 = new FMatrixRMaj(3, 3);
ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect1, rect1_F32);
ConvertMatrixData.convert(rect2, rect2_F32);
ImageDistort rectifyImageLeft =
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getLeft(), rect1_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distLeft.getImageType());
ImageDistort rectifyImageRight =
RectifyDistortImageOps.rectifyImage(param.getRight(), rect2_F32, BorderType.SKIP, distRight.getImageType());
rectifyImageLeft.apply(distLeft, rectLeft);
rectifyImageRight.apply(distRight, rectRight);
// convert for output
BufferedImage outLeft = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectLeft, null, true);
BufferedImage outRight = ConvertBufferedImage.convertTo(rectRight, null, true);
// show results and draw a horizontal line where the user clicks to see rectification easier
ListDisplayPanel panel = new ListDisplayPanel();
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, origLeft, origRight), "Original");
panel.addItem(new RectifiedPairPanel(true, outLeft, outRight), "Rectified");
ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Stereo Rectification Calibrated", true);
}
}