Difference between revisions of "Example Canny Edge"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| (2 intermediate revisions by the same user not shown) | |||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Example Code: | Example Code: | ||
* [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0. | * [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.40/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/features/ExampleCannyEdge.java ExampleCannyEdge] | ||
Concepts: | Concepts: | ||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* Demonstration of the Canny edge detection algorithm. | * Demonstration of the Canny edge detection algorithm. In this implementation the output can be a binary image and/or | ||
* a graph describing each contour. | * a graph describing each contour. | ||
* | * | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
public class ExampleCannyEdge { | public class ExampleCannyEdge { | ||
public static void main( String | public static void main( String[] args ) { | ||
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO. | BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(UtilIO.pathExample("simple_objects.jpg")); | ||
GrayU8 gray = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(image,(GrayU8)null); | GrayU8 gray = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(image, (GrayU8)null); | ||
GrayU8 edgeImage = gray.createSameShape(); | GrayU8 edgeImage = gray.createSameShape(); | ||
// Create a canny edge detector which will dynamically compute the threshold based on maximum edge intensity | // Create a canny edge detector which will dynamically compute the threshold based on maximum edge intensity | ||
// It has also been configured to save the trace as a graph. | // It has also been configured to save the trace as a graph. This is the graph created while performing | ||
// hysteresis thresholding. | // hysteresis thresholding. | ||
CannyEdge<GrayU8,GrayS16> canny = FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2,true, true, GrayU8.class, GrayS16.class); | CannyEdge<GrayU8, GrayS16> canny = FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, GrayU8.class, GrayS16.class); | ||
// The edge image is actually an optional parameter. | // The edge image is actually an optional parameter. If you don't need it just pass in null | ||
canny.process(gray,0.1f,0.3f,edgeImage); | canny.process(gray, 0.1f, 0.3f, edgeImage); | ||
// First get the contour created by canny | // First get the contour created by canny | ||
List<EdgeContour> edgeContours = canny.getContours(); | List<EdgeContour> edgeContours = canny.getContours(); | ||
// The 'edgeContours' is a tree graph that can be difficult to process. | // The 'edgeContours' is a tree graph that can be difficult to process. An alternative is to extract | ||
// the contours from the binary image, which will produce a single loop for each connected cluster of pixels. | // the contours from the binary image, which will produce a single loop for each connected cluster of pixels. | ||
// Note that you are only interested in external contours. | // Note that you are only interested in external contours. | ||
| Line 50: | Line 50: | ||
// display the results | // display the results | ||
BufferedImage visualBinary = VisualizeBinaryData.renderBinary(edgeImage, false, null); | BufferedImage visualBinary = VisualizeBinaryData.renderBinary(edgeImage, false, null); | ||
BufferedImage visualCannyContour = VisualizeBinaryData.renderContours(edgeContours,null, | BufferedImage visualCannyContour = VisualizeBinaryData.renderContours(edgeContours, null, | ||
gray.width,gray.height,null); | gray.width, gray.height, null); | ||
BufferedImage visualEdgeContour = new BufferedImage(gray.width, gray.height,BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | BufferedImage visualEdgeContour = new BufferedImage(gray.width, gray.height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB); | ||
VisualizeBinaryData.render(contours, (int[]) null, visualEdgeContour); | VisualizeBinaryData.render(contours, (int[])null, visualEdgeContour); | ||
ListDisplayPanel panel = new ListDisplayPanel(); | ListDisplayPanel panel = new ListDisplayPanel(); | ||
panel.addImage(visualBinary,"Binary Edges from Canny"); | panel.addImage(visualBinary, "Binary Edges from Canny"); | ||
panel.addImage(visualCannyContour, "Canny Trace Graph"); | panel.addImage(visualCannyContour, "Canny Trace Graph"); | ||
panel.addImage(visualEdgeContour,"Contour from Canny Binary"); | panel.addImage(visualEdgeContour, "Contour from Canny Binary"); | ||
ShowImages.showWindow(panel,"Canny Edge", true); | ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Canny Edge", true); | ||
} | } | ||
} | } | ||
</syntaxhighlight> | </syntaxhighlight> | ||
Latest revision as of 12:32, 17 January 2022
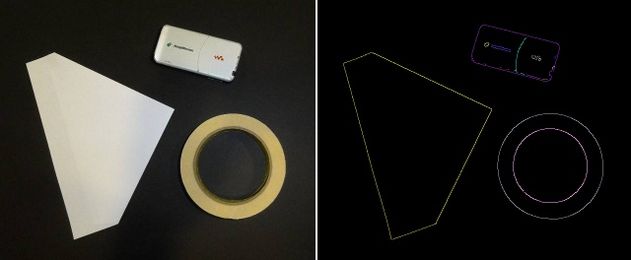
Edge or contour detection is a basic computer vision problem. The Canny edge detector is a popular algorithm for detecting edges in an image which uses hystersis thresholding. In BoofCV the Canny edge detector can produce different kinds of output. A binary image containing every pixel which is identified as an edge or a tree graph containing all the selected edge pixels.
Example Code:
Concepts:
- Object contours/edges
Relevant Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Demonstration of the Canny edge detection algorithm. In this implementation the output can be a binary image and/or
* a graph describing each contour.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleCannyEdge {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
BufferedImage image = UtilImageIO.loadImageNotNull(UtilIO.pathExample("simple_objects.jpg"));
GrayU8 gray = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(image, (GrayU8)null);
GrayU8 edgeImage = gray.createSameShape();
// Create a canny edge detector which will dynamically compute the threshold based on maximum edge intensity
// It has also been configured to save the trace as a graph. This is the graph created while performing
// hysteresis thresholding.
CannyEdge<GrayU8, GrayS16> canny = FactoryEdgeDetectors.canny(2, true, true, GrayU8.class, GrayS16.class);
// The edge image is actually an optional parameter. If you don't need it just pass in null
canny.process(gray, 0.1f, 0.3f, edgeImage);
// First get the contour created by canny
List<EdgeContour> edgeContours = canny.getContours();
// The 'edgeContours' is a tree graph that can be difficult to process. An alternative is to extract
// the contours from the binary image, which will produce a single loop for each connected cluster of pixels.
// Note that you are only interested in external contours.
List<Contour> contours = BinaryImageOps.contourExternal(edgeImage, ConnectRule.EIGHT);
// display the results
BufferedImage visualBinary = VisualizeBinaryData.renderBinary(edgeImage, false, null);
BufferedImage visualCannyContour = VisualizeBinaryData.renderContours(edgeContours, null,
gray.width, gray.height, null);
BufferedImage visualEdgeContour = new BufferedImage(gray.width, gray.height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
VisualizeBinaryData.render(contours, (int[])null, visualEdgeContour);
ListDisplayPanel panel = new ListDisplayPanel();
panel.addImage(visualBinary, "Binary Edges from Canny");
panel.addImage(visualCannyContour, "Canny Trace Graph");
panel.addImage(visualEdgeContour, "Contour from Canny Binary");
ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Canny Edge", true);
}
}