Difference between revisions of "Example Calibrate Planar Fisheye"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
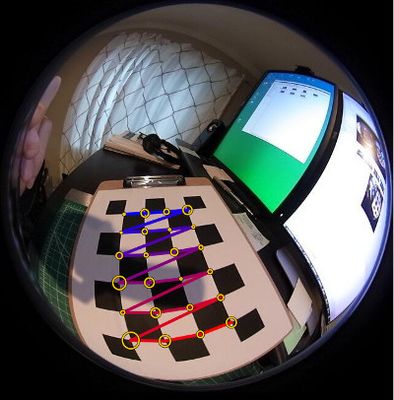
This example demonstrates how to compute the intrinsic camera parameters for a fisheye camera lens. Fisheye lenses exhibit significantly more distortion than regular lenses with a more narrow field of view. Its not unusual for a fisheye lens to have a FOV of 185 degrees. The calibration process is very similar to regular cameras. A planar calibration target is shown at different angles across the entire field of view. The main difference is the camera model. | This example demonstrates how to compute the intrinsic camera parameters for a fisheye camera lens. Fisheye lenses exhibit significantly more distortion than regular lenses with a more narrow field of view. Its not unusual for a fisheye lens to have a FOV of 185 degrees. The calibration process is very similar to regular cameras. A planar calibration target is shown at different angles across the entire field of view. The main difference is the camera model. | ||
Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0. | Example File: [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.38/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/calibration/ExampleCalibrateFisheye.java ExampleCalibrateFisheye.java] | ||
Calibration Tutorial: [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration|Wikipage]] | Calibration Tutorial: [[Tutorial_Camera_Calibration|Wikipage]] | ||
| Line 77: | Line 77: | ||
CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "fisheye.yaml"); | CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "fisheye.yaml"); | ||
calibrationAlg.printStatistics(); | calibrationAlg.printStatistics(System.out); | ||
System.out.println(); | System.out.println(); | ||
System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---"); | System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---"); | ||
Revision as of 09:01, 12 July 2021
This example demonstrates how to compute the intrinsic camera parameters for a fisheye camera lens. Fisheye lenses exhibit significantly more distortion than regular lenses with a more narrow field of view. Its not unusual for a fisheye lens to have a FOV of 185 degrees. The calibration process is very similar to regular cameras. A planar calibration target is shown at different angles across the entire field of view. The main difference is the camera model.
Example File: ExampleCalibrateFisheye.java
Calibration Tutorial: Wikipage
Concepts:
- Camera calibration
- Fisheye Lens distortion
- Intrinsic parameters
Relevant Videos:
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Example of how to calibrate a single (monocular) fisheye camera using a high level interface. This example
* for the most part follows the same routine as {@link ExampleCalibrateMonocular}. Fisheye cameras tend to require
* more images to properly calibrate. Often people will use larger calibration targets too that are easier to
* see at a distance and cover more of the fisheye's camera large FOV.
*
* @see CalibrateMonoPlanar
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleCalibrateFisheye {
public static void main( String[] args ) {
DetectorFiducialCalibration detector;
List<String> images;
// Circle based calibration targets not not recommended because the sever lens distortion will change
// the apparent location of tangent points.
// Square Grid example
// detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.squareGrid(null, new ConfigGridDimen(4, 3, 30, 30));
// images = UtilIO.listAll(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/fisheye/square_grid"));
// Chessboard Example
detector = FactoryFiducialCalibration.chessboardX(null,new ConfigGridDimen(7, 5, 30));
images = UtilIO.listAll(UtilIO.pathExample("calibration/fisheye/chessboard"));
// Declare and setup the calibration algorithm
CalibrateMonoPlanar calibrationAlg = new CalibrateMonoPlanar(detector.getLayout());
// tell it type type of target and which parameters to estimate
calibrationAlg.configureUniversalOmni( true, 2, false);
// it's also possible to fix the mirror offset parameter
// 0 = pinhole camera. 1 = fisheye
// calibrationAlg.configureUniversalOmni( true, 2, false,1.0);
for( String n : images ) {
BufferedImage input = UtilImageIO.loadImage(n);
if( input != null ) {
GrayF32 image = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(input,(GrayF32)null);
if( detector.process(image)) {
calibrationAlg.addImage(detector.getDetectedPoints().copy());
} else {
System.err.println("Failed to detect target in " + n);
}
}
}
// process and compute intrinsic parameters
CameraUniversalOmni intrinsic = calibrationAlg.process();
// save results to a file and print out
CalibrationIO.save(intrinsic, "fisheye.yaml");
calibrationAlg.printStatistics(System.out);
System.out.println();
System.out.println("--- Intrinsic Parameters ---");
System.out.println();
intrinsic.print();
}
}