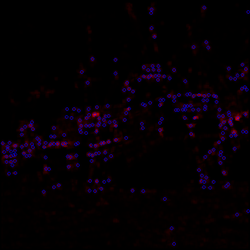Difference between revisions of "Example Non Maximum Suppression"
From BoofCV
Jump to navigationJump to searchm |
m |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
Non-maximum suppression is a class of algorithm used to find local peaks and minimums inside a feature intensity image. This example demonstrations how to use efficient algorithms inside of BoofCV to quickly find extremes. | Non-maximum suppression is a class of algorithm used to find local peaks and minimums inside a feature intensity image. This example demonstrations how to use efficient algorithms inside of BoofCV to quickly find extremes. | ||
Example Code: | Example Code: | ||
* [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0. | * [https://github.com/lessthanoptimal/BoofCV/blob/v0.38/examples/src/main/java/boofcv/examples/features/ExampleNonMaximumSupression.java ExampleNonMaximumSupression.java] | ||
Concepts: | Concepts: | ||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
<syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | <syntaxhighlight lang="java"> | ||
/** | /** | ||
* Non-maximum suppression is used to identify local maximums and/or minimums in an image feature intensity map. | * Non-maximum suppression is used to identify local maximums and/or minimums in an image feature intensity map. This | ||
* is a common step in feature detection. | * is a common step in feature detection. BoofCV includes an implementation of non-maximum suppression which is much | ||
* faster than the naive algorithm that is often used because of its ease of implementation. | * faster than the naive algorithm that is often used because of its ease of implementation. The following code | ||
* demonstrates how some of the tuning parameters affects the final output. | * demonstrates how some of the tuning parameters affects the final output. | ||
* | * | ||
| Line 38: | Line 38: | ||
NonMaxSuppression nonmax = FactoryFeatureExtractor.nonmax(new ConfigExtract(radius, threshold )); | NonMaxSuppression nonmax = FactoryFeatureExtractor.nonmax(new ConfigExtract(radius, threshold )); | ||
// We will only searching for the maximums. | // We will only searching for the maximums. Other variants will look for minimums or will exclude previous | ||
// candidate detections from being detected twice | // candidate detections from being detected twice | ||
QueueCorner maximums = new QueueCorner(); | QueueCorner maximums = new QueueCorner(); | ||
Revision as of 09:51, 12 July 2021
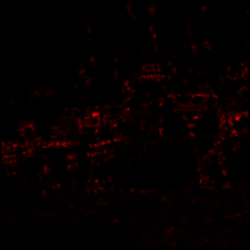
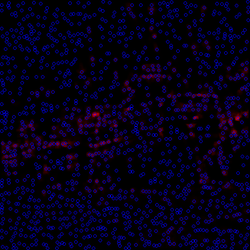
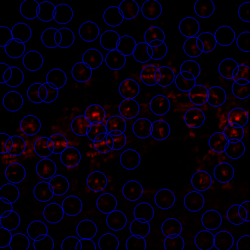
- Non-maximum suppression with different settings
Non-maximum suppression is a class of algorithm used to find local peaks and minimums inside a feature intensity image. This example demonstrations how to use efficient algorithms inside of BoofCV to quickly find extremes. Example Code:
Concepts:
- Feature detection
Related Examples:
Example Code
/**
* Non-maximum suppression is used to identify local maximums and/or minimums in an image feature intensity map. This
* is a common step in feature detection. BoofCV includes an implementation of non-maximum suppression which is much
* faster than the naive algorithm that is often used because of its ease of implementation. The following code
* demonstrates how some of the tuning parameters affects the final output.
*
* @author Peter Abeles
*/
public class ExampleNonMaximumSupression {
public static BufferedImage renderNonMax( GrayF32 intensity, int radius , float threshold) {
// Create and configure the feature detector
NonMaxSuppression nonmax = FactoryFeatureExtractor.nonmax(new ConfigExtract(radius, threshold ));
// We will only searching for the maximums. Other variants will look for minimums or will exclude previous
// candidate detections from being detected twice
QueueCorner maximums = new QueueCorner();
nonmax.process(intensity, null, null, null, maximums );
// Visualize the intensity image
BufferedImage output = new BufferedImage(intensity.width,intensity.height, BufferedImage.TYPE_INT_RGB);
VisualizeImageData.colorizeSign(intensity, output, -1);
// render each maximum with a circle
Graphics2D g2 = output.createGraphics();
g2.setColor(Color.blue);
for (int i = 0; i < maximums.size(); i++) {
Point2D_I16 c = maximums.get(i);
VisualizeFeatures.drawCircle(g2, c.x, c.y, radius);
}
return output;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
BufferedImage buffered = UtilImageIO.loadImage(UtilIO.pathExample("standard/boat.jpg"));
GrayF32 input = ConvertBufferedImage.convertFrom(buffered, (GrayF32)null);
// Compute the image gradient
GrayF32 derivX = input.createSameShape();
GrayF32 derivY = input.createSameShape();
GImageDerivativeOps.gradient(DerivativeType.SOBEL, input, derivX, derivY, BorderType.EXTENDED);
// From the gradient compute intensity of shi-tomasi features
GeneralFeatureIntensity<GrayF32,GrayF32> featureIntensity =
FactoryIntensityPoint.shiTomasi(3,false, GrayF32.class);
featureIntensity.process(input, derivX, derivY, null, null , null);
GrayF32 intensity = featureIntensity.getIntensity();
ListDisplayPanel panel = new ListDisplayPanel();
panel.addImage(buffered, "Input Image");
// hack to just show intensity - no features can be detected
panel.addImage(renderNonMax(intensity, 10, Float.MAX_VALUE), "Intensity Image");
// Detect maximums with different settings and visualize the results
panel.addImage(renderNonMax(intensity, 3, -Float.MAX_VALUE), "Radius 3");
panel.addImage(renderNonMax(intensity, 3, 30000), "Radius 3 threshold");
panel.addImage(renderNonMax(intensity, 20, -Float.MAX_VALUE), "Radius 10");
panel.addImage(renderNonMax(intensity, 20, 30000), "Radius 10 threshold");
ShowImages.showWindow(panel, "Non-Maximum Suppression", true);
}
}